Cybercriminals are ditching hacking into corporate networks and are instead using legitimate credentials to access and compromise them, with a 71% spike in cyber-attacks caused by exploiting identity, according to IBM.
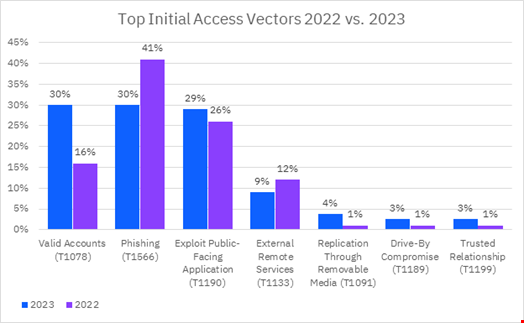
In its 2024 X-Force Threat Intelligence Index, published on February 21, 2024, IBM observed that compromising valid identities represented 30% of the total initial access vectors used in 2023.
This represents a big jump from 2022, when this method only accounted for 16% of initial access vectors.
Phishing also represented 30% of the initial access vectors used in 2023, an 11% drop compared to 2022.
There are several ways to get hold of valid accounts, including:
- Obtaining, sometimes buying, credentials and databases from previous data breaches sold on the dark web
- Or through infostealers, pieces of malware designed to steal personal and enterprise credentials, personally identifiable information and banking and crypto wallet information.
In 2023, X-Force observed a 266% increase in infostealing malware.
Businesses Need Unified Identity Access Management Solutions
Julian David, CEO of techUK, commented: “In an era marked by the growing sophistication of cybercriminals who exploit legitimate accounts to breach business defenses, IBM’s X-Force Threat Intelligence Index serves as a stark wake-up call.
In an IBM public statement, Martin Borrett, technical director of IBM Security, UK and Ireland (UKI), suggested ways to mitigate this growing threat.
“Addressing cybersecurity challenges requires a strategic approach, emphasizing the reinforcement of foundational security measures. Streamlining identity management through a unified Identity and Access Management (IAM) provider and strengthening legacy applications with modern security protocols are crucial steps in mitigating risks.
“Additionally, subjecting your system to rigorous stress tests by skilled offensive security teams proves invaluable in uncovering potential weaknesses. This insight is pivotal for crafting a robust incident response plan that engages all teams, from IT professionals to C-suite executives.”
2024 Threat Intelligence Index’s Other Key Findings
Other key findings from the 2024 X-Force Threat Intelligence Index include:
- A focus on critical infrastructure, with nearly 70% of attacks globally targeting critical infrastructure in 2023
- An 11.5% drop in ransomware attacks targeting enterprises in 2023,
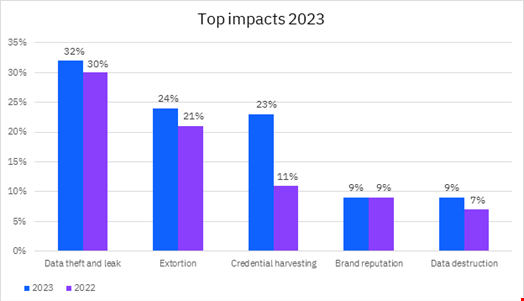
- Data theft and leak incidents as cyber-attacks’ top impact, with 32% of the global incidents observed in 2023 resulting in a data breach
- A growing trend of using legitimate tools for hacking purposes, with 32% of cyber-attacks involving this tactic
According to IBM, the most targeted region was Europe, representing 32% of global cyber-attacks in 2023.
The manufacturing sector was the most targeted industry, accounting for 25.7% of all attacks observed in 2023. Malware was used in 45% of incidents.
Finally, IBM assessed that AI hasn’t been a serious threat so far but could become one in the future.
“When a single generative AI technology approaches 50% market share or when the market consolidates to three or fewer technologies, it could trigger at-scale attacks against these platforms,” the report reads.
Charles Henderson, head of IBM X-Force, commented: “While ‘security fundamentals’ doesn’t get as many head turns as ‘AI-engineered attacks,’ it remains that enterprises’ biggest security problem boils down to the basic and known – not the novel and unknown. Identity is being used against enterprises time and time again, a problem that will worsen as adversaries invest in AI to optimize the tactic.”
The 2024 X-Force Threat Intelligence Index is based on insights and observations from monitoring over 150 billion daily security events in more than 130 countries.
In addition, data is gathered and analyzed from multiple sources within IBM, including IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence, Incident Response, X-Force Red, IBM Managed Security Services, and data provided from IBM-owned Red Hat Insights and Intezer.
